Types of Number: Essential 11+ Maths Topics Explained
- Suratna Solutions
- Aug 5
- 3 min read
Introduction
Numbers are a fundamental part of mathematics and are used in everyday life, from counting and measuring to solving problems. Let’s explore the various categories of numbers we’ll encounter in our studies.
Types of Numbers:
2.1 Natural Numbers (N):
Any number that are used as counting numbers are natural numbers.
They start from 1 and go to forever (infinity).
They do not include 0 or negative numbers.
Example: 1, 2, 3, 4, ....
2.2 Whole Numbers (W):
Whole numbers include all natural numbers plus 0.
They start from 0 and go on forever.
There are no fractions, decimals, or negatives in this set.
Example: 0, 1, 2, 3, ....
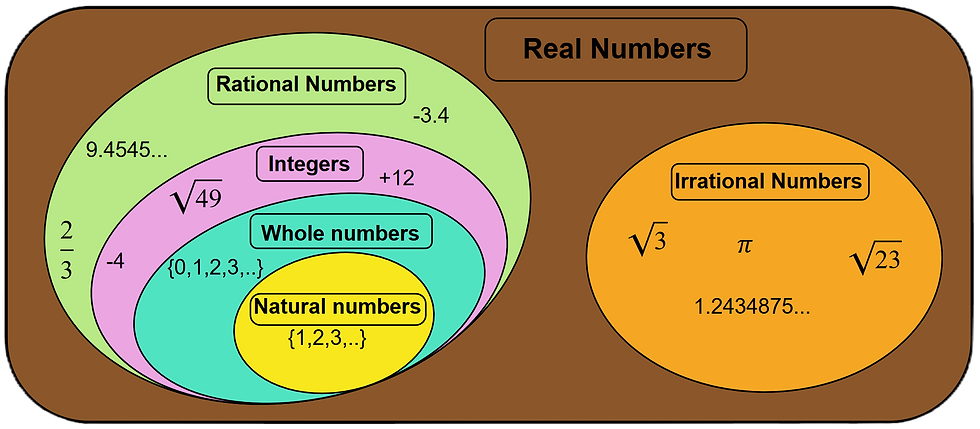
2.3 Integers (Z):
Integers include all whole numbers as well as their negative counterparts.
This set contains positive numbers, negative numbers, and 0.
No fractions or decimals are included.
Example: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ....
2.4 Rational Numbers (Q):
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction, where the numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero.
Includes all integers as they can be written as fractions.
Includes terminating decimals (e.g., 0.5) and recurring decimals (e.g., 0.333…).
Example: \( \frac{1}{2} \) , -3, 0.25, 5.333......
2.5 Irrational Numbers:
Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction. Their decimal form is non-terminating and non-recurring.
They cannot be written as exact fractions.
Common examples include square roots of non-perfect squares and certain constants.
Example: \( \sqrt{2} \), \( \pi \), 3.124576896738919
2.6 Real Numbers (R):
Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers. Essentially, they represent every number you can think of on a number line.
This set includes natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers.
Example: -2, 0, 3/4, \( \sqrt{2} \), \( \pi \)
2.7 Prime Numbers:
Prime numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that have only two factors: 1 and themselves.
They cannot be divided evenly by any other numbers except 1 and the number itself.
Example: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, ...
2.8 Composite Numbers:
Composite numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that have more than two factors.
They can be divided evenly by numbers other than 1 and themselves.
Example: 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, ...
2.9 Odd and Even Number Chart:

2.10 Even Numbers:
Even numbers are divisible by 2 without remainders.
They end in 0, 2, 4, 6, 8.
2.11 Odd Numbers:
Odd numbers are not divisible by 2 without remainders.
They end in 1, 3, 5, 7, 9.
2.12 Square numbers:
Square numbers are the product of a number that has been multiplied by itself.
Example: 2 x 2 = 4, 3 x 3 = 9, 4 x 4 = 16
\( \sqrt{4} \) can be written as \( \sqrt{2 \times 2} \) = 2

2.13 Cube numbers:
A Cube number is the product when a number has been multiplied by itself and then itself again.
Example: 2 x 2 x 2 = 8, 3 x 3 x 3 = 27, 4 x 4 x 4 = 64
\( \sqrt[3]{8} \) can be written as \( \sqrt[3]{2 \times 2 \times 2} \) = 2

2.14 Triangular Number:
A Triangular number is a number that can be shown using a pattern of dots in an equilateral triangle.
Example: 1, 3, 6, 10, ....

Example Questions for 11+ Maths Topics:
Example: Show that the number 36 is a square number.
The definition of a square number is any number that is the result of a number multiplied by itself.
So, 36 = 6 x 6
36 is a square number because it can be calculated by multiplying 6 by itself.
Example: Determine whether the number 23 is a prime number.
The definition of a prime number is any positive whole number that has only two factors, 1 and itself. The factors of 23 are 1 and 23.
23 is a prime number as it only has two factors, 1 and 23 (itself).